Visualising Solid Shapes
Visualising solid shapes explained here students of class 7 and 8 to understand the view of solid figures. Plane figures or shapes have two measurements namely length and breadth. Hence, they are called two-dimensional shapes whereas a solid object has three measurements namely length, breadth, height or depth. Hence, they are called three-dimensional shapes. Also, a solid shape occupies some space. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures can also be briefly named as 2-D and 3-D figures, respectively.
Two-dimensional and Three -dimensional Shapes
Some two-dimensional figures are shown below.
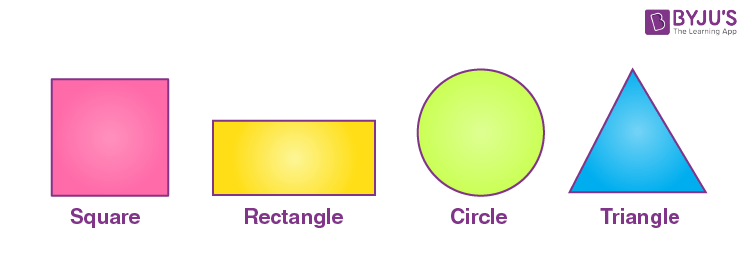
Some three-dimensional figures are shown below:
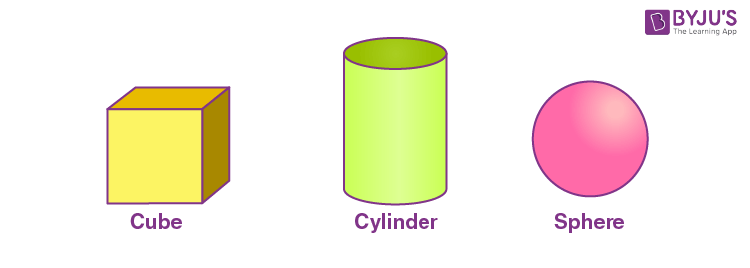
Three-dimensional figures have different numbers of faces, edges and vertices. All the flat surfaces of the figure are called faces, these faces are 2-D shapes. The line segment where the faces of three-dimensional figures meet each other is called the edge of the shape. The corners or points where the edges of the figure meet each other are called vertices (if one such point is there, then it is called a vertex).
Read more:
Parts of Solid Shapes
Consider a cuboid, the faces, edges and vertices are shown below:
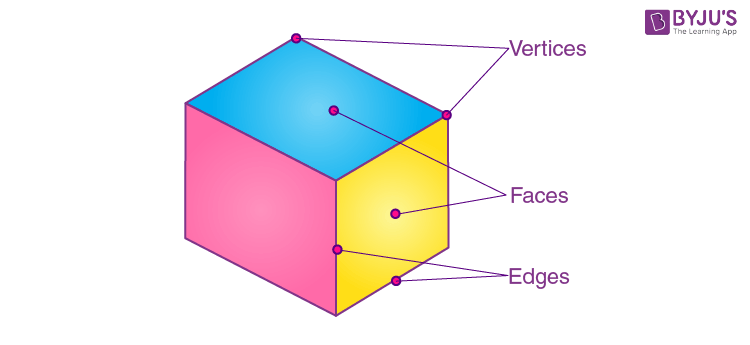
The number of faces = 6
Number of edges = 12
Number of vertices = 8
Three-dimensional shapes are further classified into two types.
- Polyhedrons (or regular polyhedrons)
- Three-dimensional figures with curved surfaces
Polyhedrons, Prism and Pyramid
| Name | Shape | Properties |
| Cube | 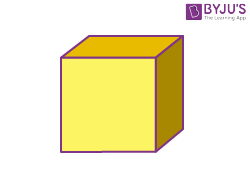 |
Faces = 6
Edges = 12 Vertices =8 |
| Cuboid | 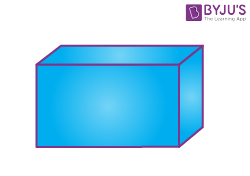 |
Faces = 6
Edges = 12 Vertices =8 |
| Prism (Triangular prism) | 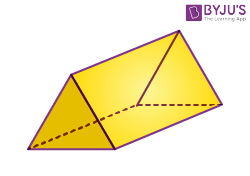 |
Faces = 5
Edges = 9 Vertices = 6 |
| Pyramid (square based pyramid) |  |
Faces = 5
Edges = 8 Vertices = 5 |
| Triangular pyramid | 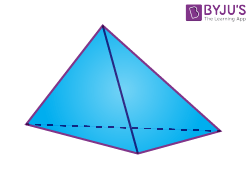 |
Faces = 4
Edges = 6 Vertices = 4 |
Three-dimensional figures with curved faces
| Name | Shape | Properties |
| Cylinder | 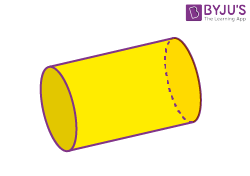 |
Faces = 3
(curved faces = 1, places surfaces =2) Edges = 2 Vertices = 0 |
| Cone |  |
Faces = 2
(curved face = 1, plane surface = 1) Edges = 2 Vertices = 1 |
| Sphere | 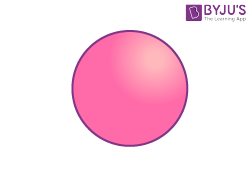 |
Faces = 1 (curved surface)
Edges = 0 Vertices = 0 |
Nets for 3-D shapes
A two-dimensional shape that can be folded to form a three-dimensional shape or a solid is referred to as a geometry net. When the surface of a three-dimensional shape is laid out flat showing each face of the shape, the obtained pattern is called a net. A solid may have different nets. In simple words, a net is an unfolded form of a 3D figure.
| Shape | Solid | Net |
| Cube | 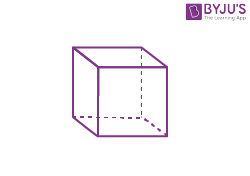 |
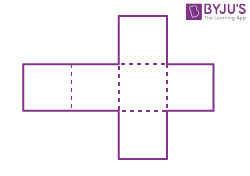 |
| Cuboid | 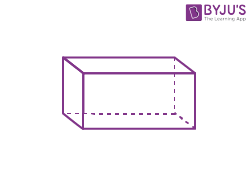 |
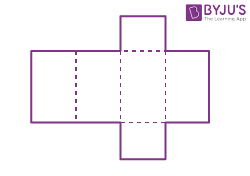 |
| Triangular prism | 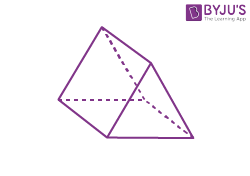 |
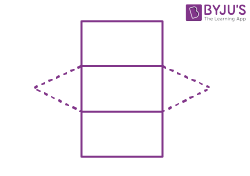 |
| Square pyramid | 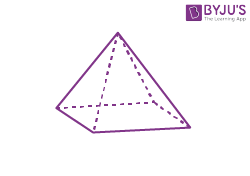 |
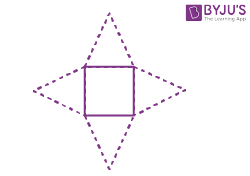 |
| Triangular pyramid | 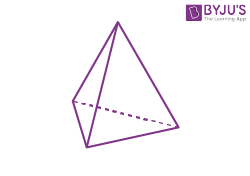 |
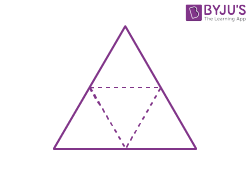 |
| Cylinder | 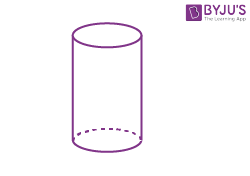 |
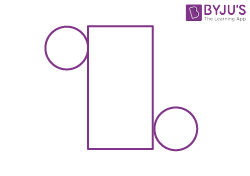 |
| Cone | 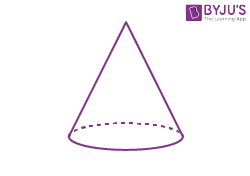 |
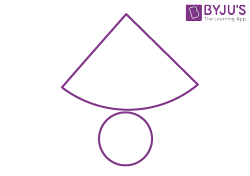 |
Video Lesson on Nets of Solids
To Know About Nets Of Solid Shapes, Watch The Below Video:

Visualising solid shapes Examples
A three-dimensional object or shape can look differently from different positions (or sides) so they can be drawn from different perspectives, this is called visualising a solid shape. For example, views of a hut and a solid with three cubes from different sides are given below.
Example 1:

As shown in the above, the front view of a hut is the combination of a square with a conical top, side view and top view is the combination of two rectangular surfaces.
Example 2:
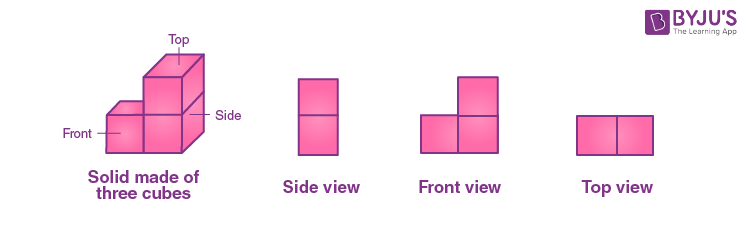
In the above figure, one side of a solid has two square surfaces which are vertically connected, front view gas three square surfaces in L shape and top view has two square surfaces which are horizontally connected.
Related Articles
Find questions and solutions for visualising solid shapes concepts in the below given links.