Binary Number System
A binary number system is one of the four types of number system. In computer applications, where binary numbers are represented by only two symbols or digits, i.e. 0 (zero) and 1(one). The binary numbers here are expressed in the base-2 numeral system. For example, (101)2 is a binary number. Each digit in this system is said to be a bit. Learn about the number system here.
| Table of Contents: |
Number System is a way to represent numbers in computer architecture. There are four different types of the number system, such as:
- Binary number system (base 2)
- Octal number system (base 8)
- Decimal number system(base 10)
- Hexadecimal number system (base 16).
In this article, let us discuss what is a binary number system, conversion from one system to other systems, table, positions, binary operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, uses and solved examples in detail.
What is a Binary Number System?
Binary Number System: According to digital electronics and mathematics, a binary number is defined as a number that is expressed in the binary system or base 2 numeral system. It describes numeric values by two separate symbols; 1 (one) and 0 (zero). The base-2 system is the positional notation with 2 as a radix.
The binary system is applied internally by almost all latest computers and computer-based devices because of its direct implementation in electronic circuits using logic gates. Every digit is referred to as a bit.
Example: Convert 4 in binary.
Solution:
4 in binary is (100)2.
Here, 4 is represented in the decimal number system, where we can represent the number using the digits from 0-9. However, in a binary number system, we use only two digits, such as 0 and 1.
Now, let’s discuss how to convert 4 in binary number system. The following steps help to convert 4 in binary.
Step 1: First, divide the number 4 by 2. Use the integer quotient obtained in this step as the dividend for the next step. Continue this step, until the quotient becomes 0.
|
Dividend |
Remainder |
|
4/2 = 2 |
0 |
|
2/2 = 1 |
0 |
|
1/2 = 0 |
1 |
Step 2: Now, write the remainder in reverse chronological order. (i.e from bottom to top).
Here, the Least Significant Bit (LSB) is 0 and the Most Significant Bit (MSB) is 1.
Hence, the decimal number 4 in binary is 1002
So, if we want to find how many bits does 4 in binary have? we have to count the number of zeros and ones.
So, 4 in binary is 1002. Here, there are 2 zeroes and 1 one. Hence, we have 3 bits.
Therefore, the number of bits does 4 in binary have is 3.
What is Bit in Binary Number?
A single binary digit is called a “Bit”. A binary number consists of several bits. Examples are:
- 10101 is a five-bit binary number
- 101 is a three-bit binary number
- 100001 is a six-bit binary number
Facts to Remember:
|
Binary Numbers Table
Some of the binary notations of lists of decimal numbers from 1 to 30, are mentioned in the below list.
| Number | Binary Number | Number | Binary Number | Number | Binary Number |
| 1 | 1 | 11 | 1011 | 21 | 10101 |
| 2 | 10 | 12 | 1100 | 22 | 10110 |
| 3 | 11 | 13 | 1101 | 23 | 10111 |
| 4 | 100 | 14 | 1110 | 24 | 11000 |
| 5 | 101 | 15 | 1111 | 25 | 11001 |
| 6 | 110 | 16 | 10000 | 26 | 11010 |
| 7 | 111 | 17 | 10001 | 27 | 11011 |
| 8 | 1000 | 18 | 10010 | 28 | 11100 |
| 9 | 1001 | 19 | 10011 | 29 | 11101 |
| 10 | 1010 | 20 | 10100 | 30 | 11110 |
How to Calculate Binary Numbers
For example, the number to be operated is 1235.
| Thousands | Hundreds | Tens | Ones |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
This indicates,
1235 = 1 × 1000 + 2 × 100 + 3 × 10 + 5 × 1
Given,
| 1000 | = 103 = 10 × 10 × 10 |
| 100 | = 102 = 10 × 10 |
| 10 | = 101 = 10 |
| 1 | = 100 (any value to the exponent zero is one) |
The above table can be described as,
| Thousands | Hundreds | Tens | Ones |
| 103 | 102 | 101 | 100 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
Hence,
1235 = 1 × 1000 + 2 × 100 + 3 × 10 + 5 × 1
= 1 × 103 + 2 × 102 + 3 × 101 + 5 × 100
The decimal number system operates in base 10, wherein the digits 0-9 represent numbers. In binary system operates in base 2 and the digits 0-1 represent numbers, and the base is known as radix. Put differently, and the above table can also be shown in the following manner.
| Thousands | Hundreds | Tens | Ones | |
| Decimal | 103 | 102 | 101 | 100 |
| Binary | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
We place the digits in columns 100, 101 and so on in base 10. When there is a need to put a value higher than 9 in the form of 10(n+1) for instance, to add 10 to column 100, you need to add 1 to the column 101.
We place the digits in columns 20, 21 and so on in base 2. To place a value that is higher than 1 in 2n, you need to add 2(n+1). For instance, to add 3 to column 20, you need to add 1 to column 21.
Position in Binary Number System
In the Binary system, we have ones, twos, fours etc…
For example 1011.110
It is shown like this:
1 × 8 + 0 × 4 + 1 × 2 + 1 + 1 × ½ + 1 × ¼ + 0 × 1⁄8
= 11.75 in Decimal
To show the values greater than or less than one, the numbers can be placed to the left or right of the point.
For 10.1, 10 is a whole number on the left side of the decimal, and as we move more left, the number place gets bigger (Twice).
The first digit on the right is always Halves ½ and as we move more right, the number gets smaller (half as big).
In the example given above:
- “10” shows ‘2’ in decimal.
- “.1” shows ‘half’.
- So, “10.1” in binary is 2.5 in decimal.
Binary Arithmetic Operations
Like we perform the arithmetic operations in numerals, in the same way, we can perform addition, subtraction, multiplication and division operations on Binary numbers. Let us learn them one by one.
Binary Addition
Adding two binary numbers will give us a binary number itself. It is the simplest method. Addition of two single-digit binary number is given in the table below.
| Binary Numbers | Addition | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0; Carry →1 |
Let us take an example of two binary numbers and add them.
For example: Add 11012 and 10012.
Solution: 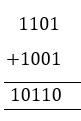
Binary Subtraction
Subtracting two binary numbers will give us a binary number itself. It is also a straightforward method. Subtraction of two single-digit binary number is given in the table below.
| Binary Numbers | Subtraction | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1; Borrow 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Let us take an example of two binary numbers and subtract them.
Example: Subtract 11012, and 10102.
Solution: 11012 – 10102 = 00112
Binary Multiplication
The multiplication process is the same for the binary numbers as it is for numerals. Let us understand it with example.
Example: Multiply 11012 and 10102.
Binary Division
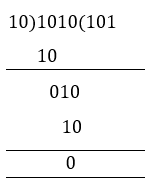
The binary division is similar to the decimal number division method. We will learn with an example here.
Example: Divide 10102 by 102
Uses of Binary Number System
Binary numbers are commonly used in computer applications. All the coding and languages in computers such as C, C++, Java, etc. use binary digits 0 and 1 to write a program or encode any digital data. The computer understands only the coded language. Therefore these 2-digit number system is used to represent a set of data or information in discrete bits of information.
Problems and Solutions
Let us practice some of the problems for better understanding:
Question 1: What is binary number 1.1 in decimal?
Solution:
Step 1: 1 on the left-hand side is on the one’s position, so it’s 1.
Step 2: The one on the right-hand side is in halves, so it’s
1 × ½
Step 3: so, 1.1 = 1.5 in decimal.
Question 2: Write 10.112 in Decimal?
Solution:
10.11 = 1 x (2)1 + 0 (2)0 + 1 (½)1 + 1(½)2
= 2 + 0 + ½ + ½
= 2.75
So, 10.11 is 2.75 in Decimal.
Keep visiting BYJU’S to explore and learn more such Math-related topics in a fun and engaging way.
Frequently Asked Questions on Binary Number System
What is a binary number system?
What is a bit?
How to convert a decimal number into a binary number? Give an example.
13 ÷ 2: 6 and remainder 1
6 ÷ 2: 3 and remainder 0
3 ÷ 2: 1 and remainder 1
1 ÷ 2: 0 and remainder 1
Now we take the bits from the last remainder to first remainder, i.e.(MSB to LSB). Hence,
1310 = 11012