Properties of Rational Numbers
To know the properties of rational numbers, we will consider here the general properties such as associative, commutative, distributive and closure properties, which are also defined for integers. Rational numbers are the numbers which can be represented in the form of p/q, where q is not equal to 0. Basically, the rational numbers are the fractions which can be represented in the number line. Let us go through all the properties here.
What are the properties of rational numbers?
The word rational has evolved from the word ratio. In general, rational numbers are those numbers that can be expressed in the form of p/q, in which both p and q are integers and q≠0. The properties of rational numbers are:
- Closure Property
- Commutative Property
- Associative Property
- Distributive Property
- Identity Property
- Inverse Property
Closure property
For two rational numbers say x and y the results of addition, subtraction and multiplication operations give a rational number. We can say that rational numbers are closed under addition, subtraction and multiplication. For example:
- (7/6)+(2/5) = 47/30
- (5/6) – (1/3) = 1/2
- (2/5). (3/7) = 6/35
Do you know why division is not under closure property?
The division is not under closure property because division by zero is not defined. We can also say that except ‘0’ all numbers are closed under division.
Commutative Property
For rational numbers, addition and multiplication are commutative.
Commutative law of addition: a+b = b+a
Commutative law of multiplication: a×b = b×a
For example:
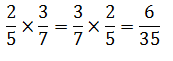
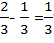
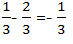
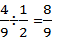
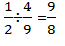
Associative Property
Rational numbers follow the associative property for addition and multiplication.
Suppose x, y and z are rational, then for addition: x+(y+z)=(x+y)+z
For multiplication: x(yz)=(xy)z.
Example: 1/2 + (1/4 + 2/3) = (1/2 + 1/4) + 2/3
⇒ 17/12 = 17/12
And in case of multiplication;
1/2 x (1/4 x 2/3) = (1/2 x 1/4) x 2/3
⇒ 2/24 = 2/24
⇒1/12 = 1/12
Distributive Property
The distributive property states, if a, b and c are three rational numbers, then;
a x (b+c) = (a x b) + (a x c)
Example: 1/2 x (1/2 + 1/4) = (1/2 x 1/2) + (1/2 x 1/4)
LHS = 1/2 x (1/2 + 1/4) = 3/8
RHS = (1/2 x 1/2) + (1/2 x 1/4) = 3/8
Hence, proved
Identity and Inverse Properties of Rational Numbers
Identity Property: 0 is an additive identity and 1 is a multiplicative identity for rational numbers.
Examples:
- 1/2 + 0 = 1/2 [Additive Identity]
- 1/2 x 1 = 1/2 [Multiplicative Identity]
Inverse Property: For a rational number x/y, the additive inverse is -x/y and y/x is the multiplicative inverse.
Examples:
The additive inverse of 1/3 is -1/3. Hence, 1/3 + (-1/3) = 0
The multiplicative inverse of 1/3 is 3. Hence, 1/3 x 3 = 1
Video Lesson

To learn more about other topics download BYJU’S – The Learning App and watch interactive videos. Also, take free tests to practise for exams.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are the important properties of rational numbers?
When two rational numbers are added then it is equal to?
What is the distributive property of rational numbers?
a x (b+c) = (a x b) + (a x c)